Your cart is empty
Shop our products
Solar panels are becoming increasingly popular for generating electricity for homes and businesses.
These solar panels work by converting sunlight into electrical energy through a process known as the photovoltaic effect. But how are solar panels actually made?
In this article, we'll look at the process of manufacturing solar panels, from the raw materials to the finished product.
Raw Materials
The production of solar panels commences with sourcing the raw materials, a crucial aspect that can impact the overall efficiency and longevity of the panels.
The primary raw material used in solar panels is silicon, which constitutes about 25% of the earth's crust.
However, it is essential to obtain silicon with high purity levels of 99.9999% or more, for optimal performance of the solar panels.
The high-purity silicon is usually derived from quartz, a ubiquitous mineral in the earth'searth's crust that requires complex processing to extract the desired silicon.
Other materials utilized in the construction of solar panels include aluminium, which is used to make the frame that holds the panels, and tempered glass, which serves as a protective layer for the solar cells.
Moreover, several chemicals play vital roles in the manufacturing process, such as doping agents like boron and phosphorus, which are necessary for creating the p-n junction, a fundamental component responsible for converting sunlight into electricity.
Manufacturing Process
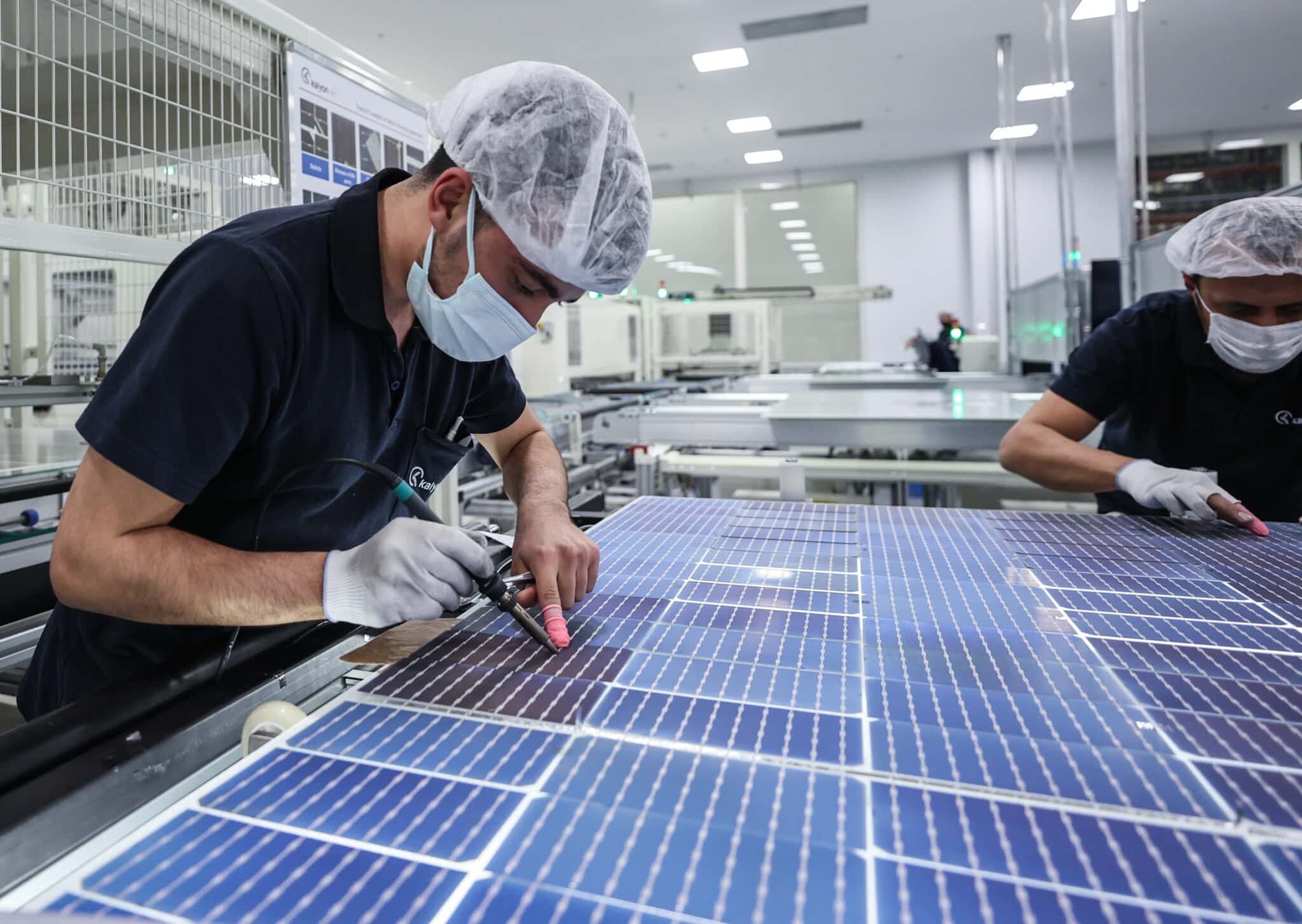

Once the raw materials have been gathered, the manufacturing process begins. Here is a step-by-step guide to how solar panels are made:
Silicon Ingot Production
The first step is to produce silicon ingots. This involves melting the raw silicon and then cooling it down slowly to form a large, cylindrical crystal. The ingot is then cut into thin wafers using a specialized saw.
Wafer Cleaning
The wafers are then cleaned extensively to remove any potential impurities that may have been introduced during the slicing process. This is done using a combination of chemicals and high-pressure water.
Doping
Doping involves adding impurities to the silicon to create a p-n junction. This is what allows the solar cell to generate electricity when exposed to sunlight. Boron and phosphorus are the two most commonly used dopants.
Texturing
The surface of the wafer is then textured to increase its surface area. This is done using a chemical etching process that creates tiny bumps and pits on the surface of the wafer.
Anti-Reflective Coating
An anti-reflective coating is applied to the surface of the wafer to reduce the amount of light that is reflected away from the cell. This allows more light to be absorbed by the cell, increasing its efficiency.
Electrical Contacts
Electrical contacts are then added to the top and bottom of the cell to allow the electricity generated by the cell to be collected and used. These contacts are made from a thin layer of metal, usually silver or aluminium.
Cell Assembly
The individual solar cells are then assembled into a larger module. This is done by placing the cells between two sheets of glass and sealing them together with a special adhesive. The module is then wired to allow the electricity generated by the cells to be collected and used.
Quality Control
Before the solar panels are shipped, they need to pass a series of quality control tests to ensure that they meet industry standards. These tests include checking for defects, measuring the efficiency of the cells, and testing the electrical connections.
Shipping
The last step is shipping the solar panels to their final destination. This can be a residential or commercial customer, a solar farm, or a distribution centre.
Are Solar Panel Materials Expensive?
 The cost of solar panel materials varies, and really all depends on certain factors, such as the quality of the materials being used, the manufacturing process, and the market demand.
The cost of solar panel materials varies, and really all depends on certain factors, such as the quality of the materials being used, the manufacturing process, and the market demand.
The primary material used in solar panels is silicon, and the cost of silicon can vary based on its purity level. Higher-purity silicon is generally more expensive to produce than lower-grade silicon, and this can impact the overall cost of solar panels.
Other materials used in solar panel production, such as aluminum and tempered glass, are generally less expensive than silicon.
However, the cost of these materials can still impact the overall cost of the solar panels, particularly if higher-quality or specialized materials are used.
The cost of solar panel materials is just one component of the overall cost of solar panel production.
The manufacturing process, labour costs, and other expenses can also impact the final price of solar panels.
Additionally, the cost of solar panels can vary depending on the market demand and availability of incentives or subsidies.
Overall, while the cost of solar panel materials can impact the final price of solar panels, the benefits of generating clean, renewable energy and reducing dependence on fossil fuels can make solar panel installations a worthwhile investment in the long run.
Final Thoughts
Solar panels are a fantastic way to generate clean energy from the sun.
Manufacturing solar panels involves several steps, from the extraction of raw materials to the assembly of the final product.
By understanding the manufacturing process, we can better appreciate the technology that makes solar power possible and the importance of investing in renewable energy sources.
Shop products from this article
You May Also Like

What Does a 30% Federal Solar Tax Credit Mean and How to Apply?
Governments around the world are offering programs that encourage homeowners to switch to solar energy. Among the most notable programs is the 30% Federal Solar Tax Credit. It reduces your...

Deadly Flooding Devastates U.S. South and Midwest — What You Need to Know