Your cart is empty
Shop our productsNeed to turn down the lights, change the temperature, monitor your security cameras, or watch a movie? All of it remotely, too? A smart home is a way of connecting your gadgets and appliances using IoT and a central device. So that you can control everything either through your phone or simply by speaking commands, and scale it up for smart buildings that crank up energy savings.
In this article, we'll tell you what a smart home system is, its components and functionality, what you actually gain with it, and where things get difficult. We'll also cover how smart energy ecosystems tie into your power setup, and the way smart homes connect with EMS and the larger power grid. So, keep scrolling!

What Is a Smart Home?
We'll begin by defining what a smart house is exactly. A smart home is a residence where the daily chores are automated through internet-connected appliances to increase security, comfort, and energy efficiency.
It is like giving your house a brain and nervous system, whereby the brain is the main central hub or app that runs everything. The nervous system consists of intelligent devices that connect and communicate with each other.
Basic Elements of a Smart Home
There are three pillars of a smart house, namely, smart devices, a hub and protocols, and a control interface. Here's how these pillars tie with each other to function as a whole system:
-
Smart Devices
Smart gadgets automate everyday appliances independently. An example would be smart thermostats such as Nest and Ecobee. These conserve energy by turning the heat or AC on and off to your preference, without any manual adjustments. There are also smart lights, such as Philips Hue or Lutron. You can adjust the color, dim the lights, set up schedules, and control everything right from your phone or just by verbal commands.
Then there are security cameras like Arlo and smart locks like August. When you are not present, they monitor events, send motion warnings, and enable you to open the door without fumbling for keys. Even appliances are stepping up. Fridges track what's inside, ovens preheat before you even walk in the door, and robot vacuums like Roomba just manage the cleaning all by themselves.
-
Hubs & Protocols
View the hub as your intelligent home's brain. It groups all together. Indeed, your devices can communicate directly with Wi-Fi. However, you have a greater degree of control with a smart hub such as Samsung SmartThings, Amazon Echo, or Apple HomePod Mini. These centers employ their own unique networks to synchronize everything. WiFi, Zigbee, Z-Wave, or Thread—all the hubs have a language of their own to connect all your smart appliances.
-
Connectivity and Automation
This is where the magic happens: constant data sharing enables automation. Devices are always communicating data, such as motion sensors, door sensors, or temperature sensors, via a hub or through the cloud, and act automatically. Automation lets your home run on schedules and routines you set.
You control your smart home mainly through apps and voice assistants. Most devices have their own smartphone app, although many of them can be connected to a single central app that is easier to control. Voice assistants, such as Alexa, Google Assistant, or Siri, can also be utilized. They are able to command devices without looking with the bare minimum, like "Turn off the lights" or "Set the temperature."
For example, your porch lamp may come on at nightfall and go off at daybreak. You are also able to make intelligent triggers depending on sensors or preferences. A motion sensor might dim hallway lights after 10 PM. A "Good Morning" routine could turn on lights, adjust the temperature, and start the coffee when your alarm goes off.

How Smart Homes Function?
A smart home functions by linking devices in a network where they communicate, share data, and follow commands. This system depends on two main factors. The communication protocols that connect devices, and whether control happens locally or through the cloud. Here's how these two variables tie together:
-
The Communication Layer
As mentioned earlier, protocols are the "languages" smart devices use to communicate with each other and the central controller. The protocol type affects the speed, dependability, and consumption of your home system. The most popular one is Wi-Fi, which links equipment to your router. It is quick and installs easily, yet it consumes more power, slows your network, and requires an internet connection.
In contrast, low-power mesh networks like Zigbee and Z-Wave protocols can each cover a larger distance with additional mesh networking between devices. Thread is a more recent low-latency protocol, which also forms a high-speed, self-healing mesh network that remains dependable in the event of one node going offline. Zigbee, Z-wave, and Thread all require a hub to access the internet.
-
The Control Layer
The control layer determines where your smart home processes commands, in the cloud or locally. With cloud control, your commands go from your phone to the internet and back to the device, which is popular for beginners and allows remote access. However, it stops functioning if your internet goes down.
Whereas local control keeps everything within your home, using a hub or device to process commands directly. This makes it faster and more dependable, even during power cuts. Many systems now use a hybrid setup, combining cloud control for remote access and voice commands with local control for core automations.
Smart Home Systems in the Real World
The following are real-life examples of how the communication and control layers can be used to create an intelligent automation system:
Example 1: The Self-Learning Thermostat (e.g., Nest)
With the assistance of Zigbee or Thread, a thermostat like Nest collects temperature, humidity, and your habits and links up with the rest of the sensors. This information is transferred to the cloud, which in turn learns about your routine and the desired temperatures. The new schedule is then sent back to the thermostat, which is then able to correct itself and save energy without the need for human intervention.
Example 2: Motion-Triggered Security Alert
An intelligent security camera records when it picks up significant movement, and it can easily recognize individuals in the area to minimize the number of false alarms. When it authenticates an individual, it sends it to the cloud, which in turn sends a notification to your phone to go and see the live feed. Meanwhile, the incident can also prompt a localized automation by a hub, such as the activation of porch lights upon a command, to prevent intruders without depending on the internet.

Benefits of Smart Homes
With a smart home, everyday life is easier. This is because a smart house allows automating all the processes and controlling your house remotely in order to make it more comfortable and convenient. Here's how:
-
Convenience
Smart homes give you remote control of your devices and automatically simplify your daily life schedule. With your phone, you may activate or deactivate lights and locks or control the temperature.
Moreover, time management lets you plan such things as making coffee early or opening blinds in the morning. A "Good Night" order can also switch off lights and lock doors at once. With voice control, you may easily manage your house without raising a hand with Google commands to illuminate a light or play some music.
-
Security
Smart technology offers real-time monitoring and control, hence improving interior house security. You will immediately get alerts of odd activity, including someone opening a window or someone knocking on your door.
Smart locks further let you give guests or service providers temporary digital keys, therefore getting rid of the need for actual keys. Another way of scaring away intruders is to program your lights or TVs to switch off and on when you are not at home, so that it appears that someone is at home.
-
Electricity Savings
Smart houses can be useful in saving electricity through automation that reduces bills and wastage of energy. The use of smart thermostats such as Nest or Ecobee reduces the use of electricity when you are away by controlling heating and cooling based on your schedule.
While smart lights are automatically switched off when no one is present in the room, or outdoor lighting is turned off when it is sunrise. Smart plugs can also stop "vampire power" by cutting electricity to devices that use energy even when turned off.
| Benefit | How It Works | Examples |
| Convenience | Automates tasks and allows remote control of devices. | Control lights, locks, and thermostats via phone; schedule routines; and use voice commands for hands-free control. |
| Security | Provides real-time monitoring, alerts, and access management. | Instant notifications for unusual activity, smart locks with temporary keys, and scheduled lights/TVs to deter intruders. |
| Energy Savings | Optimizes energy use to reduce waste and lower bills. | Smart thermostats adjust temperature; smart lights turn off when not in use; smart plugs eliminate "vampire power." |

What Is a Smart Home Energy Ecosystem?
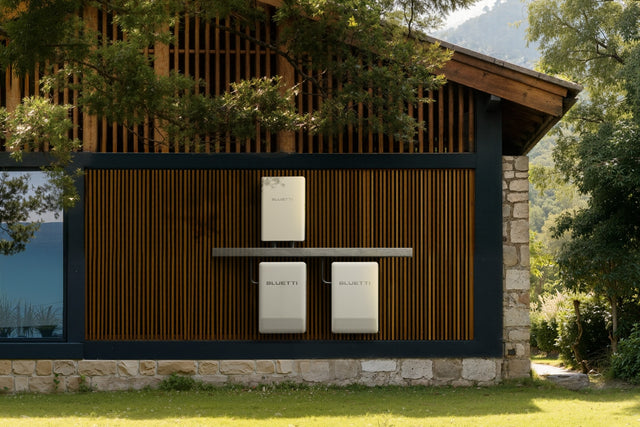
A smart home energy system links everything, like solar panels, smart meters, and batteries. So your home produces and consumes energy more cleverly. Solar panels soak up sunshine and transform it into clean electricity. Whereas smart meters monitor your consumption and even let you sell surplus power back to the grid. Backup batteries like the BLUETTI Apex 300 store the leftover energy, so you've got power at night or when the lights go out.
All this isn't just about saving money. It makes your home more efficient and less dependent on grid energy. The Apex 300 will continuously measure and regulate the flow of energy by automatically utilizing solar energy when it is accessible, storing excess energy, or selling it back to the grid. Such an arrangement reduces electricity bills, improves the utilization of solar, and ensures that your home is not left without power even when there is a blackout.
Limitations of a Smart Home System
Although smart homes are associated with numerous advantages, they also have limitations like increased cost, privacy, security, and complexity of setup. The following are the primary drawbacks one should be aware of before investing money into the innovation:
-
Risk of Data Security and Privacy
An unprotected smart home can be an easy target for hacking or illegal entry. Hackers could spy on people using cameras, abuse smart speakers, or even open doors. The best way to remain safe is to use a very strong and unique password, two-factor authentication, and ensure your devices are securely encrypted in order to block intruders.
-
Expensive Upfront Set-up and Maintenance
The convenience of smart homes often comes with a high cost. The cost of installing a full smart lighting, security, and climate control system can run into thousands in terms of the devices, hubs, and even installation expenses. Some systems also have monthly subscriptions for features like cloud video storage or advanced automation.
-
The Data Privacy vs. Cloud AI Trade-Off
The major concern of smart homes is the privacy vs. convenience trade-off. Numerous devices transmit to cloud servers for AI capabilities and automation, such as voice commands, routines, and energy usage. This may put your privacy or data at risk of breach. Privacy-oriented systems that store data on a local drive are more secure but more rigorous to configure and less sophisticated.
-
The Technical Learning Curve
Creating and operating a smart home may be a difficult process for someone who does not know the technical context. The installation of equipment from different brands, connecting hubs, and troubleshooting network problems may be complex. Even when it has been set up, automations and settings require time to learn, and not all the features might be utilized by all users.

Integrating Power Solutions in Smart Homes

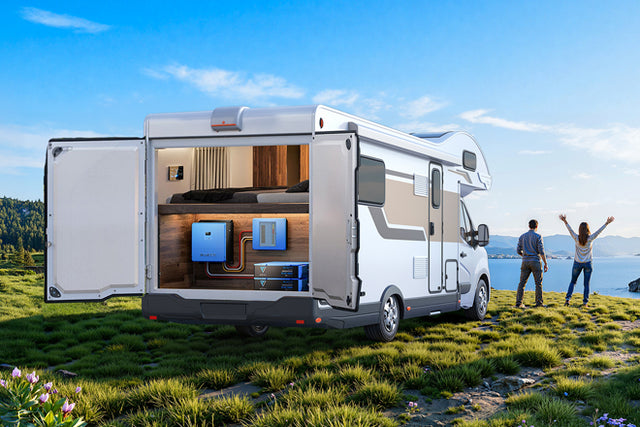
The integration of power solutions with your smart home system is very important in case of blackouts or off-grid living. A portable power station for home backup, such as the BLUETTI Elite 100 V2, is an example of such a power solution. It's ideal for an emergency, for camping, or to power small devices. The unit has a 1,024Wh battery, a 1,800W AC output, and 10ms UPS switchover.
It can charge quickly via wall, solar, car charger, and dual AC + solar input. Moreover, the unit supports app monitoring and feeds devices like smartphones, laptops, mini-fridges, CPAP machines, and small kitchen appliances. You can charge the unit with AC input fully in 45 minutes, and with 1000W of solar input, in 70 minutes. But using a car charger, you are able to charge the Elite 100 V2 6x quicker.
For complete house energy independence and to cut electricity expenses, a high-capacity, modular home backup system like the BLUETTI Apex 300 is the perfect candidate. It has a 2,764.8 Wh battery, a 3,840W AC output, and smart features like Peak-Load Shifting, immediate 0 ms UPS, and app control. The unit can integrate with solar panels and home circuits to provide backup power when there is a blackout and automated management of the energy to save on bills.

Upgrading the unit to 58kWh of capacity and 11.52 kW of output is another possibility. So, it can power a smart home system totally off-grid or during an extended electricity failure. The Apex 300 supports AC, solar, dual AC + solar, and a 120/240V generator input. You can hit up to 80% in 40 minutes with 2400W solar input, 100% in 60 minutes with 3840 AC + solar, and via a generator.
With AC, it can charge up to 80% in 45 minutes and can reach up to 30kW with SolarX 4K and AT-1 expansion. The BLUETTI app allows you to control performance and also enables Peak-Load Shifting in the Apex 300. When electricity is cheap, the unit will recharge the battery, and when it becomes costly, it will provide the stored energy to your house. Though you may not have the solar panels, the electricity will cost you less in such a case.
How Smart Homes Interact With EMS or the Grid?
The power grid, smart homes, and Home Energy Management System (EMS) all function in tandem to transform the homes into active components of a smart energy network. This system can increase stability and efficiency by providing real-time interaction between the energy providers and consumers. Here's how it all comes together:
-
The Smart Home as a Grid Participant
A smart home with an EMS, solar panels, and a battery becomes a "prosumer," both producing and using energy. Your home will be able to share power and support the grid through a two-way communication between the utility and a smart meter.
The utility can request that your home switch to battery power or use a bit less electricity during times of high demand, usually with a monetary incentive. When lots of houses do that, they become a virtual power plant, serving to prevent power blackouts as well as minimize dependence on polluting backup generators.
-
The Role of the Home EMS
The Home EMS is the main manager between your smart devices, energy systems, and the power grid. It tracks real-time data of energy use, solar output, battery activity, and grid electricity charges to make smart choices to improve efficiency and minimize spending.
As an example, Home EMS can provide charging to batteries during off-peak times. Then, it utilizes solar energy first before dispatching excess charge to the grid. The EMS can also regulate energy consumption automatically when the utility asks it to do so, all while maintaining comfort in your home.
A Real-Life Situation of EMS on a Scorching Summer Day
It is sizzling, and the grid is overloaded on a summer day, and electricity prices have shot up. Thus, the utility sends a demand-response signal to the smart homes via the smart meter. The Home EMS also responds automatically by switching to battery power rather than the grid, slightly elevating the thermostat.
So as to reduce the use of AC, and halt unnecessary processes such as the dishwasher. Consequently, your house consumes less power when electricity is in peak demand, which saves money and contributes to stabilizing the grid. An integrated system of many of these smart homes forms a more sustainable and efficient energy system.

FAQs
-
Will smart devices function with other brands?
When your smart devices come from different brands, getting them to function together can be complicated. But if you stick to one platform, like Alexa, Google Assistant, HomeKit, or Matter, the devices might function fine. Another way is to connect every appliance to a central hub, like Samsung SmartThings, since it supports different protocols. This gives the gadgets the privilege of operating communally within a single app and following the same automations.
-
Are smart home systems expensive to set up and run?
A smart home can cost as little as a few dollars when it's just one device. If you want a fully installed smart home system, you're probably looking at thousands of dollars. The hardware isn't cheap, but over time, smart devices actually help cut expenses by keeping your heating, cooling, and lighting in check. Day-to-day, they consume meager electricity, just enough to retain smart devices' operations.
-
Is it worth putting a smart system in an apartment or rental home?
Yes. The portable smart devices can be easily used by the renters without any modifications to the property. Smart speakers, portable lights, clever plugs, non-permanent video doorbells, wireless sensors, and more may all be included among these. But install equipment that calls for hardwiring or permanent modifications only with your landlord's permission. You should look at solutions to increase convenience without damaging your security deposit.
-
What is the benefit of having a central hub in a smart residence?
A smart home's brain is its central hub, which causes gadgets using several protocols like Zigbee and Z-Wave to all run within one system. Since it carries out instructions locally, it speeds up and improves dependability. Hence, the automations remain functional even when the internet is offline. Hubs also allow sophisticated routines on a variety of devices, and can be controlled via a single application.
Conclusion
"What is a smart home exactly, and what are its functions and advantages?" We've answered that to the best of our knowledge in this post. It is an interconnected network that provides convenience, security, and energy conservation through connecting devices, automatic routines, and smart energy ecosystems. The advantages of a home system are efficiency, remote control, and increased comfort. Nonetheless, it is also associated with such issues as cost, privacy, and complexity of setup.
The BLUETTI Apex 300 is the best choice to make your smart home independent of the electricity grid and to be able to back up the home with a dependable power supply. It boasts modular capacity, Peak-Load Shifting, and integration with solar panels. For portable power or emergency power for little smart gadgets, the BLUETTI Elite 100 V2 is a fast-charging power solution with solar capabilities. Both BLUETTI units will guarantee that your smart house is effective, dependable, and resilient during an off-grid or blackout.
Shop products from this article
You May Also Like

HMI Demystified: The User-Friendly Interface for Easy Energy Storage Management

BLUETTI App Guide: Features for Easy Power Station Management from Your Phone